Based on statistics, it has been proven that more than one billion people are infected with worms, which are popularly called worms. However, these indicators are conditional, because they were established based on the number of people who sought help from specialists diagnosing helminth infections.
Every person (regardless of age and gender) encounters worms at least once in their life, but many people are simply unaware of their infection and continue to transmit worms to others. In the initial stages of infection, they do not cause discomfort, but in case of mass infections, they can cause toxic poisoning and even death. Therefore, you need to know what worms are, what they look like in the body, and how to fight the acquired disease.
Doctors have already examined many "uninvited guests" in the body of animals and people that overwhelm the immune system and can make holes in the blood vessels if they gnaw on them. This has serious consequences in the form of erosions and other diseases, so helminthic infections must be treated first.
Types of worms
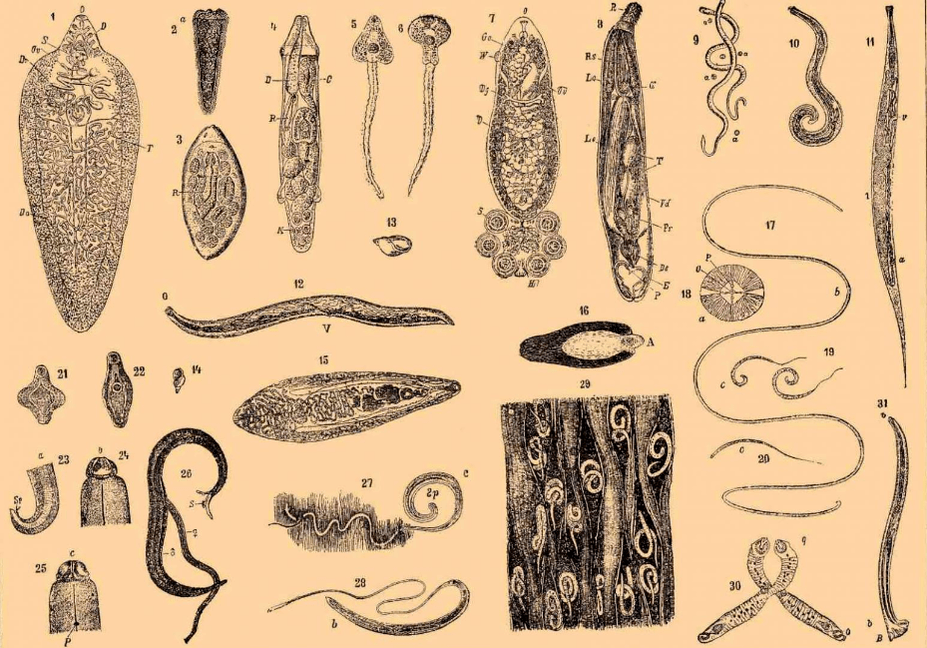
Among the many types of worms, the greatest damage to the body can be caused by 3 classes of worms: roundworms, roundworms and tapeworms. Let's see what these worms look like in humans.
Roundworms
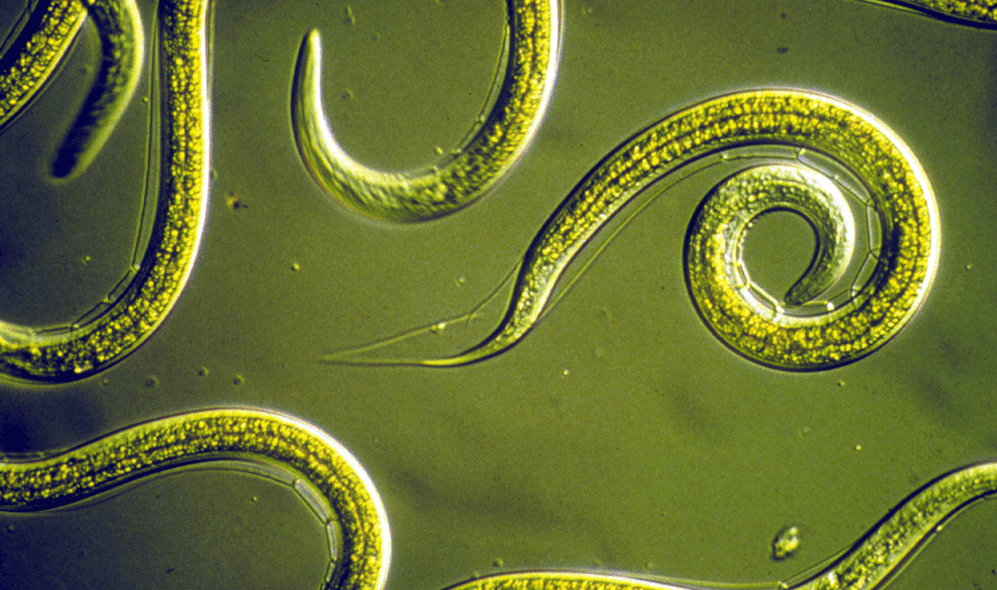
The class of nematodes is commonly called nematodes. This is one of the most common types of worms that infect the human body. However, in addition to parasitic nematodes, there are also free-living nematodes, so these are not found in the human body.
The picture shows the body of nematodes, which is characterized by a round shape, which is why they are classified as roundworms. They have a thin and elongated body with pointed ends on both sides.
During the examination, the worms belonging to this class are most often found in the human body: whipworm, roundworm, trichina (Trichinella) and pinworm. This type of worms in people can be seen in the picture.
Male roundwormsits body length is shorter than that of females. Females can grow up to 40 centimeters. Cylindrical worms are localized in the intestines and poison the body with toxic substances. If a large amount of parasites accumulates in this cavity, they are able to close the lumen of the intestine and impede its patency. If you refuse treatment, the invasion can lead to death, because the excess substances are no longer removed from the body, and the poisoning reaches its limit.
PinwormsThey bark in a smaller size than roundworms. Their body length does not exceed 1 cm. These representatives reproduce actively, because living in the small intestine and rectum, they have access to the anus, and crawling out from there, the females lay larvae on the femoral part, on the anus, between the buttocks. A scoop can lay up to 15, 000 eggs at a time, causing skin irritation. Then the infected person begins to scratch the irritant, contributing to the spread of helminths to others. Worms are most often found in children, so it is necessary to check for worm eggs in kindergartens and schools, as well as in institutions with a large number of people.
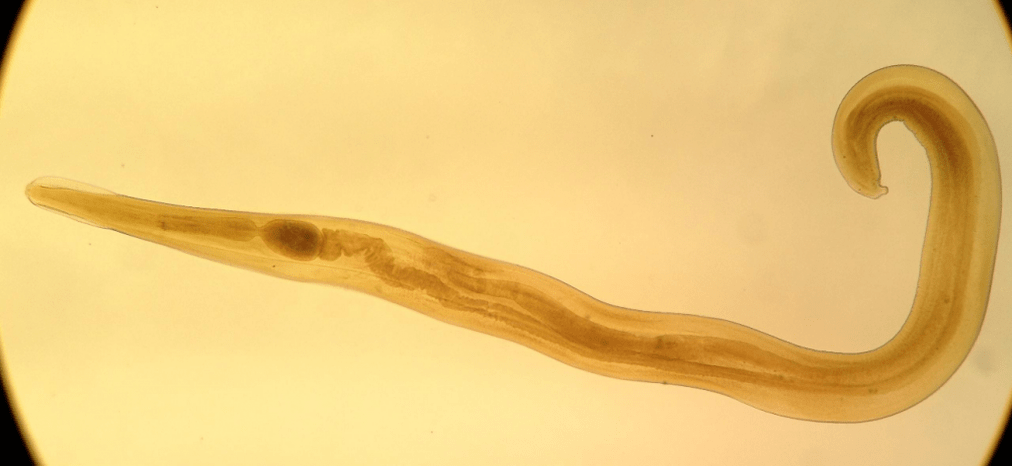
WhipwormIt is an equally dangerous parasite, as the female worm lays 3, 000-4, 000 eggs per day. When the worm has reached sexual maturity, it has a thread-like front end that makes up 2/3 of the body length and a thick gray-pink rear end with transverse stripes. The average length of the worm is 3-5 cm. The tails of female and male representatives are different: in females it is bent, in males it is spiral.
The danger of whipworm infection is that this worm penetrates the mucous membrane and deep layers. It can affect smooth muscle and feed on tissue fluid.
Pea worma particularly dangerous parasite that lives in the muscles and intestinal walls of humans. Visually, the worm looks like a long, twisted thread that reaches 4. 5 mm and 1. 6 mm in diameter. The vital activity of such a helminth can lead to the death of the carrier if therapeutic measures are not taken in time.
Flukes
.png)
Many people are interested in what parasites in the human body of the fluke class look like (photo). In medical practice, they are called trematodes, but the most interesting thing is that they do not suck anything from the body, but feed on mucus, blood and what the worms pass through the affected area. Trematodes can grow up to 1. 5 meters in length and can be found not only in the intestines, but also in other organs (even in the conjunctival sac).
However, worms belonging to the class of flukes are able to attach to the intestinal wall and thus resist passing out with random stools. These parasites have functional digestive and reproductive systems, but minimal respiratory and circulatory systems.
Tapeworms
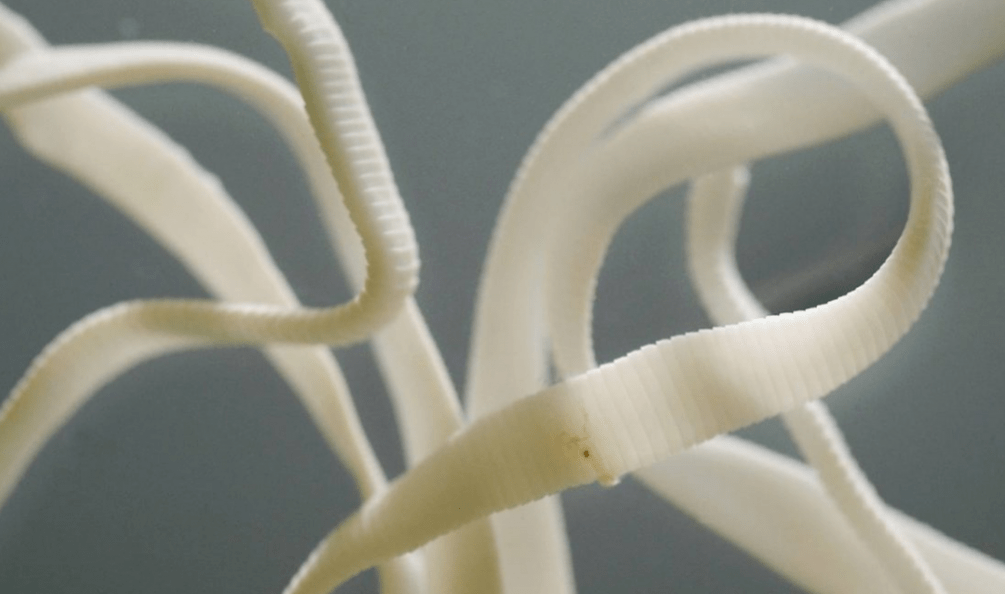

Tapeworms- the class of flatworms, which is divided into tapeworms and tapeworms. These individuals rarely enter the human body directly. Infection is most often caused by eating fish infected with these parasites, but in animals they only occur in the larval stage and mature inside an individual with a backbone.
The body of parasites belonging to this class has a special anatomical structure, so the head of the worm is only used for attachment to the intestinal wall, and this worm uses the whole body to get food. The food of their host serves as food for tapeworms, but intestinal worms are not digested by gastric juice because they release a substance called antikinase.
Despite the similarity of these worms, it is imperative to distinguish them when making a diagnosis in order to determine the appropriate treatment method.
Tapeworms have 2 suction cups on their heads, which allow them to securely attach to the intestinal wall, unlike representatives of tapeworms, which have 4 gripping teeth. The tapeworm's body length can reach 18 meters and occupies the entire length of the small intestine.
How do you get infected with these worms?

The spread of helminths begins with phase 1, which is characterized by the entry of worm eggs into the human body. They then hatch, become larvae (phase 2) and move throughout the body until they settle in organs or systems, but most often remain in the intestines. In phase 3, the worms are no longer able to migrate throughout the body, but are able to reproduce and infect the healthy population.
Despite the diversity and characteristics of worms, the infection can be combined. This indicates the possibility of simultaneous stay in the digestive system or organs of different types of worms without interfering with each other.
Infection caused by worms can occur in 3 ways:
- Person to person.
- Through the earth.
- Following a raw diet and consuming poorly processed foods, especially vegetables and fruits, herbs.
Signs of infection
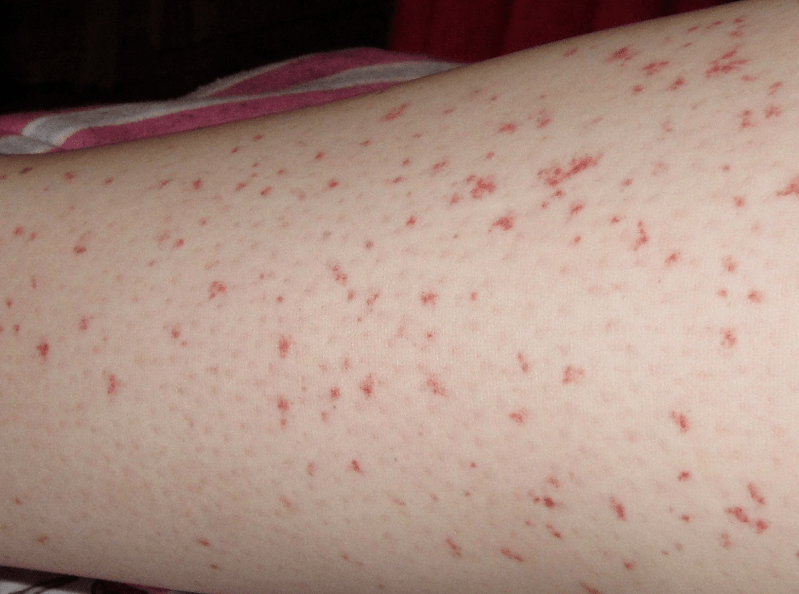
The signs of helminth infection can be very different, but first of all, it is necessary to start from the stage of the infection:
- Acute. It lasts up to 20 days. In this case, extensive allergic reactions of unknown origin can be observed. This is due to the immune system reacting to a stimulus. The allergy causes a rash and clinical blood tests show higher than normal levels of eosinophils.
- Acquired. In this stage, the disease can develop in 2-3 years. In this case, the symptoms depend on the organ in which the parasites live, their number, and how much they have damaged tissue walls or body systems. In severe situations, they cause inflammation, and fast-growing species can have fatal consequences.
It is very important to know what type of parasites they look like, because sometimes dead adults can be passed along with feces, and then based on the description of their appearance, you can speed up the diagnosis and quickly choose a treatment method.
Timely recognition of helminths plays an important role in human life, as not all parasites are able to exist practically harmless in the body. At least 1-2 times a year, it is recommended to have the whole family undergo a medical examination, wash your hands before eating, eat only well-processed foods and use folk anthelmintics as a preventive measure: clove or wormwood powder, walnut shell tincture.






































